Pressurization shaft is an essential component of the safety systems in high-rise buildings. They work by maintaining a positive pressure in stairwells and other areas of the building during an emergency to prevent smoke and fire from entering and spreading through the building. In this article, we’ll explore what pressurization shafts are, how they work, and the benefits they offer. We’ll also examine the different applications of pressurization shafts in high-rise buildings.
What are Pressurization Shafts?
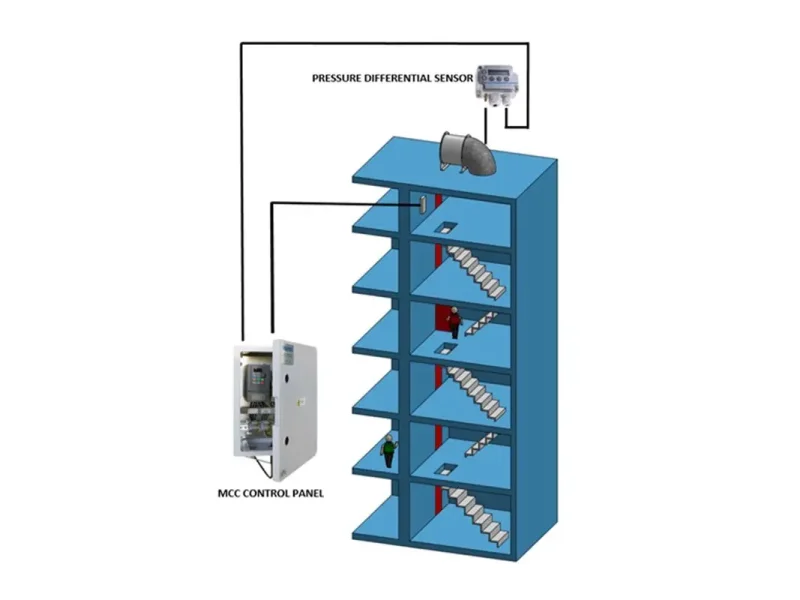
Pressurization shafts, also known as smoke control shafts, are vertical spaces in high-rise buildings that are designed to maintain a positive pressure in stairwells, corridors, and other areas during an emergency. These shafts work by drawing air from the building’s common areas and forcing it into the pressurization shafts, creating a barrier of pressurized air that prevents smoke and fire from entering and spreading through the building.
Pressurization shafts are typically made of fire-resistant materials and are designed to contain smoke and fire within the shaft. They are equipped with fire dampers that automatically close in the event of a fire, preventing the spread of smoke and fire through the shaft.
How do Pressurization Shafts Work?
Pressurization shafts work by maintaining a positive pressure in stairwells and other areas of the building during an emergency. This positive pressure prevents smoke and fire from entering the areas and spreading throughout the building.
The pressurization system consists of fans, ductwork, and dampers. The fans draw air from the building’s common areas, such as hallways and lobbies, and force it into the pressurization shafts through ductwork. The dampers prevent smoke and fire from entering the shafts and spreading through the building.
During an emergency, the pressurization system is activated automatically, either by a smoke detector or manually by building personnel. The pressurized air creates a barrier that prevents smoke and fire from entering the stairwells and other areas of the building.
Benefits of Pressurization Shafts
Pressurization shafts offer a range of benefits, including:
Increased safety: Pressurization shafts play a critical role in ensuring the safety of building occupants during an emergency, preventing smoke and fire from entering and spreading through the building.
Compliance with building codes: Many building codes require the installation of pressurization systems in high-rise buildings to ensure the safety of occupants during an emergency.
Cost-effective: Installing a pressurization system is a cost-effective way to comply with building codes and ensure the safety of building occupants.
Energy-efficient: Pressurization shafts are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy than other types of ventilation systems, making them an energy-efficient solution for high-rise buildings.
Applications of Pressurization Shafts
Pressurization shafts are primarily used in high-rise buildings to maintain a positive pressure in stairwells, corridors, and other areas during an emergency. They are required by many building codes and are an essential part of the safety systems in high-rise buildings.
In addition to their primary application, pressurization shafts can also be used in other applications, such as:
Smoke control systems: Pressurization shafts can be used as part of a smoke control system to prevent smoke and fire from spreading through a building.
HVAC systems: Pressurization shafts can be integrated with HVAC systems to distribute conditioned air evenly throughout a building.
Industrial applications: Pressurization shafts can be used in industrial applications where positive pressure is required, such as clean rooms or manufacturing facilities.
Choosing the Right Pressurization Shaft
When selecting a pressurization shaft, it’s important to consider factors such as the size of the building, the number of floors, and the required airflow rate. The airflow rate is determined by the size and number of fans required to maintain a positive pressure in the stairwells and other areas during an emergency.
It’s also important to consider the location of the pressurization shaft. They should be located in a separate mechanical room away from the stairwells and other areas to prevent damage in the event of a fire. The shaft location should also provide easy access for maintenance and inspection.
Additionally, the materials used in the construction of the pressurization shaft are critical. They should be fire-resistant and able to withstand high temperatures and pressures to prevent the spread of smoke and fire.
Conclusion
Pressurization shafts are an essential part of the safety systems in high-rise buildings. They maintain a positive pressure in stairwells, corridors, and other areas during an emergency, preventing smoke and fire from entering and spreading through the building. With their increased safety, compliance with building codes, cost-effectiveness, and energy efficiency, pressurization shafts are a critical component of many high-rise buildings.
When selecting a pressurization shaft, it’s important to consider factors such as the size of the building, the number of floors, and the required airflow rate. Choosing the right shaft and control system is essential to ensure maximum efficiency and performance.
With their ability to maintain a positive pressure in stairwells and prevent the spread of smoke and fire, pressurization shafts are a crucial component of the safety systems in high-rise buildings. Their importance should not be underestimated, and building owners and managers should ensure that they are properly installed, maintained, and inspected to ensure the safety of building occupants.
